Minimum Selling Price (MSP) Estimator
This tool uses an algorithm called pyTEA to
estimate MSP of biofuels and bioproduct. Details of
pyTEA
and its prediction error are provided here.
pyTEA is a process-based simulation model designed to
approximate costs
of major supply and production stages for a given
molecule.
While lacking the nuance and precision of
industry-grade software such as SuperPro Designer
or Aspen Plus, it aims to roughly emulate the methods of
these programs and generate comparable outputs
in a fast and lightweight manner.
To validate the accuracy of pyTEA
we first ran 2,000
simulation trials of a SuperPro model for bioethanol
production from lignocellulosic biomass.
For each trial, values of the
input parameters were drawn randomly from their
respective
probability distributions. We treat the MSP values
generated
SuperPro in these trials as the 'ground truth' as they
are
derived from the most precise mechanistic method
available.
We then used pyTEA to make predictions on each of the
2,000 simulation trials. The scatterplots below show the
correlations between the SuperPro MSP values for each
trial
and the corresponding pyTEA prediction
for the same set of input parameter values.
pyTEA
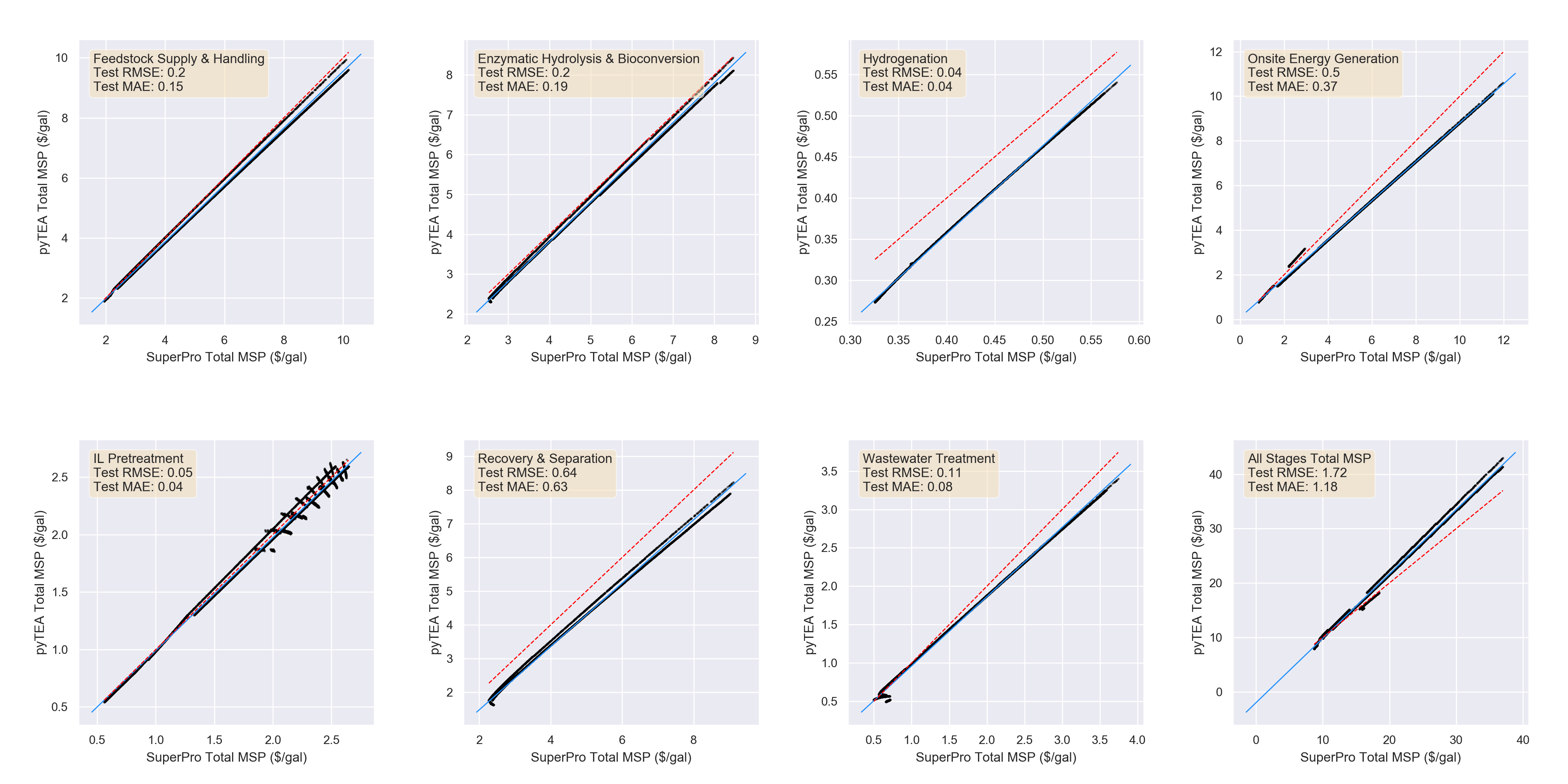
A greater clustering of points around the y = x line
(dashed red) in these plots indicates closer agreement
between
predicted and actual values, and thus higher prediction
accuracy.
Quantitatively, we rely on
Mean Absolute Error
(MAE) as our primary metric of model prediction error.
Conceptually, MAE simply measures the average difference
between
predicted and ground truth values and therefore offers
easily
interpretable error margins in the same units as the
target
variable. In terms of total MSP, pyTEA achieves an MAE
of
1.18 $/gal.
 Final Product:
Final Product:
